Challenge details
I heard you could malloc into scary places, so im adding a check to prevent that from ever happening!
Introduction
This challenge implements a heap note system with malloc/free/print/write operations on glibc 2.39. A limit check preventing chunks above the heap boundary via sbrk(0) is present upon allocation:
1 | chunks[idx] = malloc(sz); |
The main vulnerability is an off by null bug in the write function, overflowing a null byte into the next chunk:
1 | case 4: // write to chunks |
Furthermore, chunks are not zeroed on allocation, enabling data leaks. Standard operations include malloc up to 0xf8 bytes.
Exploitation
Exploit the off by null bug to create overlapping chunks, then leverage tcache poisoning - instead of allocating chunks beyond the boundary and trying to read and write to it, allocate a chunk inside the tcache_perthread_struct (first chunk). Abuse this primitive to leak stack and binary addresses by redirecting allocations to arbitrary memory locations and reading the entry pointer, then finally overwrite a chunk pointer in the global chunks array to point to _IO_2_1_stdout_ and perform a file struct exploit to gain shell access.
Step 1: Heap Leak
First, obtain a heap leak by abusing the fact that the chunks don’t get zeroed out on allocation:
1 | free(malloc(0, 0x38)) |
Step 2: Overlapping Chunks via Off by Null Vuln
Create overlapping chunks by abusing the off by null to modify chunk sizes:
1 | b = malloc(1, 0x28) |
Step 3: Libc Leak
Fill tcache and free to unsorted bin:
1 | x = [malloc(i + 3, 0xF8) for i in range(7)] |
Step 4: Writing into tcache_perthread_struct
1 | typedef struct tcache_perthread_struct |
This is the key part - poison the tcache to create a chunk inside the tcache perthread struct, specifically in the entries array:
1 | pad = malloc(4, 0x28) |
This will allow controlling the entries for tcachebin.
Step 5: Stack and ELF Leaks
Leaking is done by allocating a chunk at an arbitrary location (the __libc_argv pointer in libc for stack leak, and an address on the stack pointing to the binary for elf leak) and reading the entry pointer from the struct.
It’s also needed to free a chunk before to satisfy this condition:
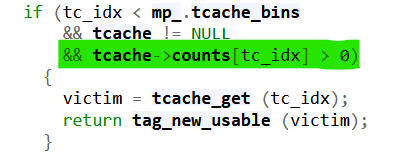
1 | free(malloc(15, 0x18)) |
Step 6: FSOP for RCE
Finally, overwrite a 0xf8-sized chunk pointer to point to stdout and perform FSOP:
1 | fsop_chunk = malloc(4, 0xf8) # a big chunk is needed to be able to fit the file struct |
This works because the memory space checking is done only when allocating chunks.
Proof
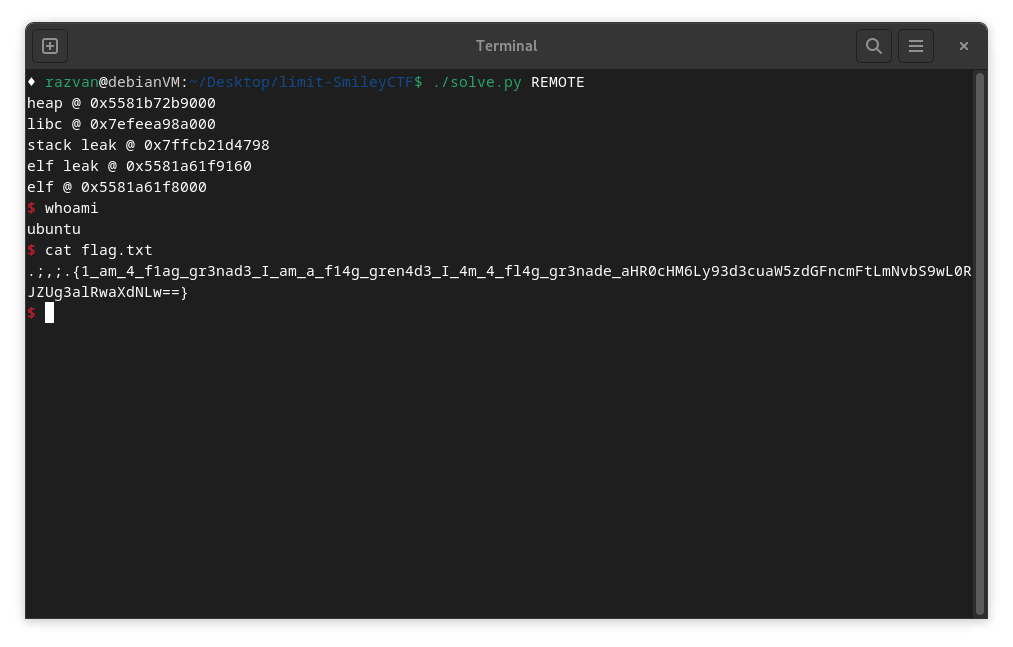
Full Exploit
1 | #!/usr/bin/python3 |